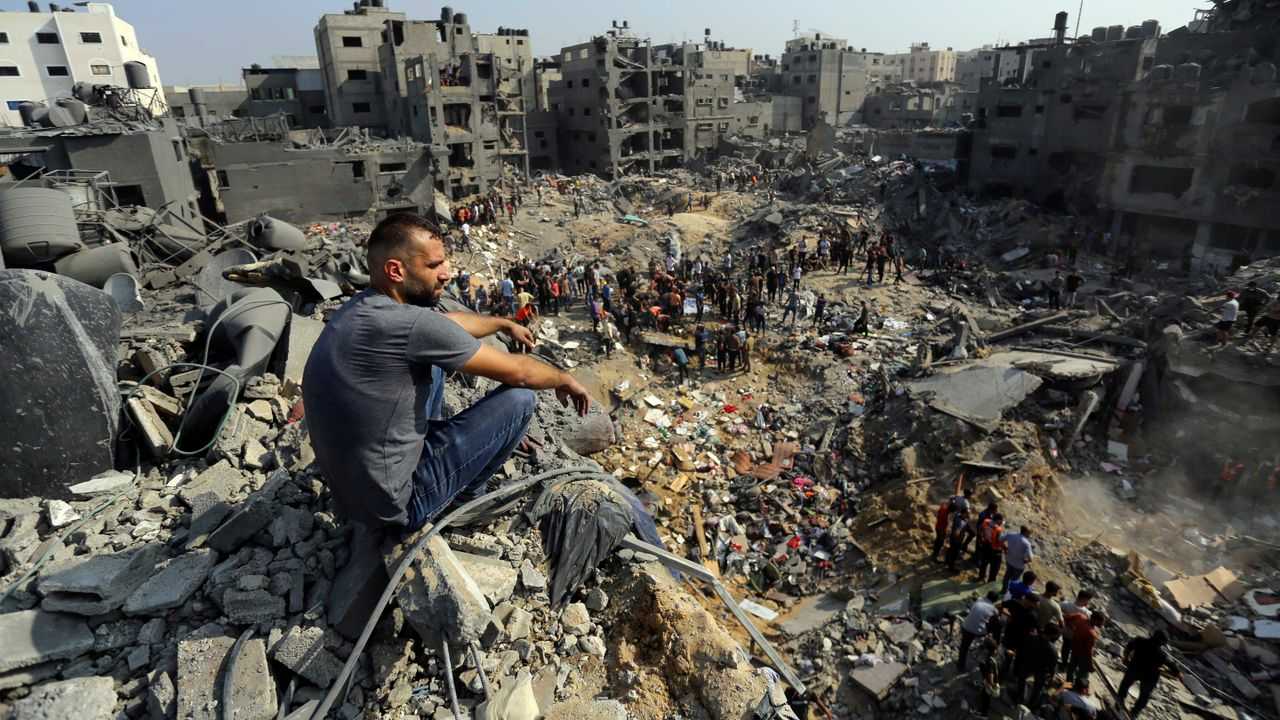
මෙහි පලවන්නේ ලෝක සමාජවාදී වෙබ් අඩවියේ 2023 අගෝස්තු 21 දින ඉංග්රීසියෙන් පලවූ This week in history: August 21-27 යන ඉතිහාසය පිලිබඳ විශේෂාංග තීරුවේ සිංහල පරිවර්තනය යි. පරිවර්තනය මිගාර මල්වත්ත විසිනි.
මීට වසර 25 කට පෙර, වසර 50 කට පෙර, වසර 75 කට පෙර සහ වසර 100 කට පෙර මෙම සතිය තුළ සිදු වූ වැදගත් ඓතිහාසික සිදුවීම් මෙම තීරුවේ පල කෙරේ.
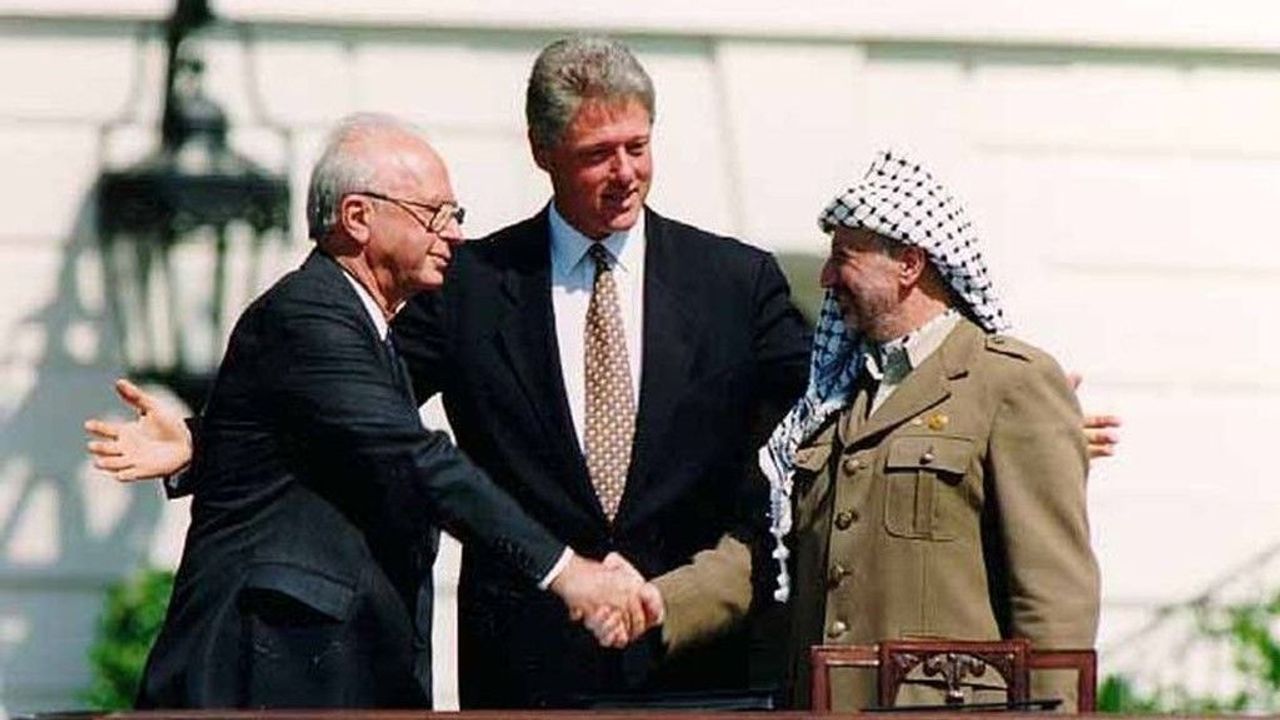
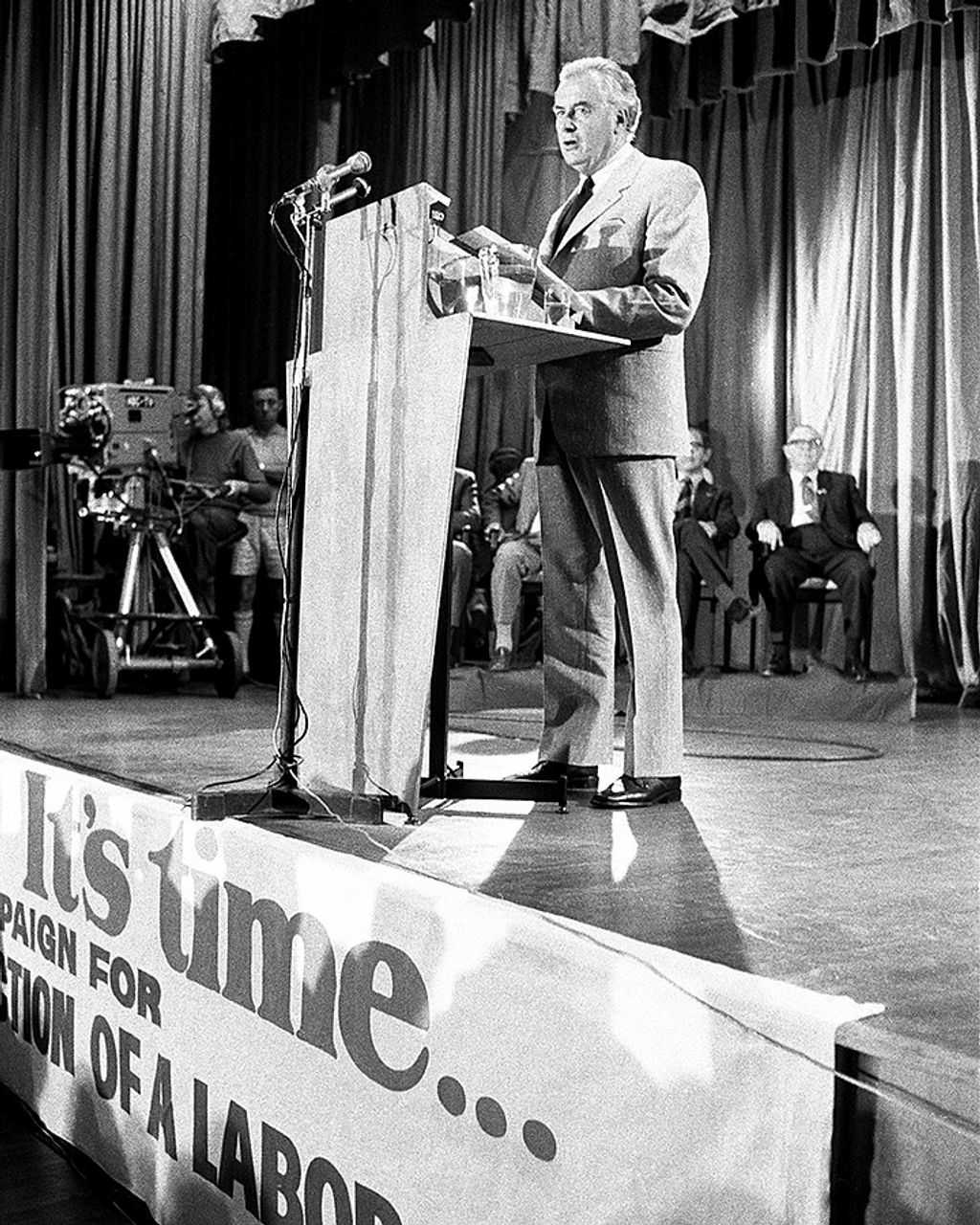
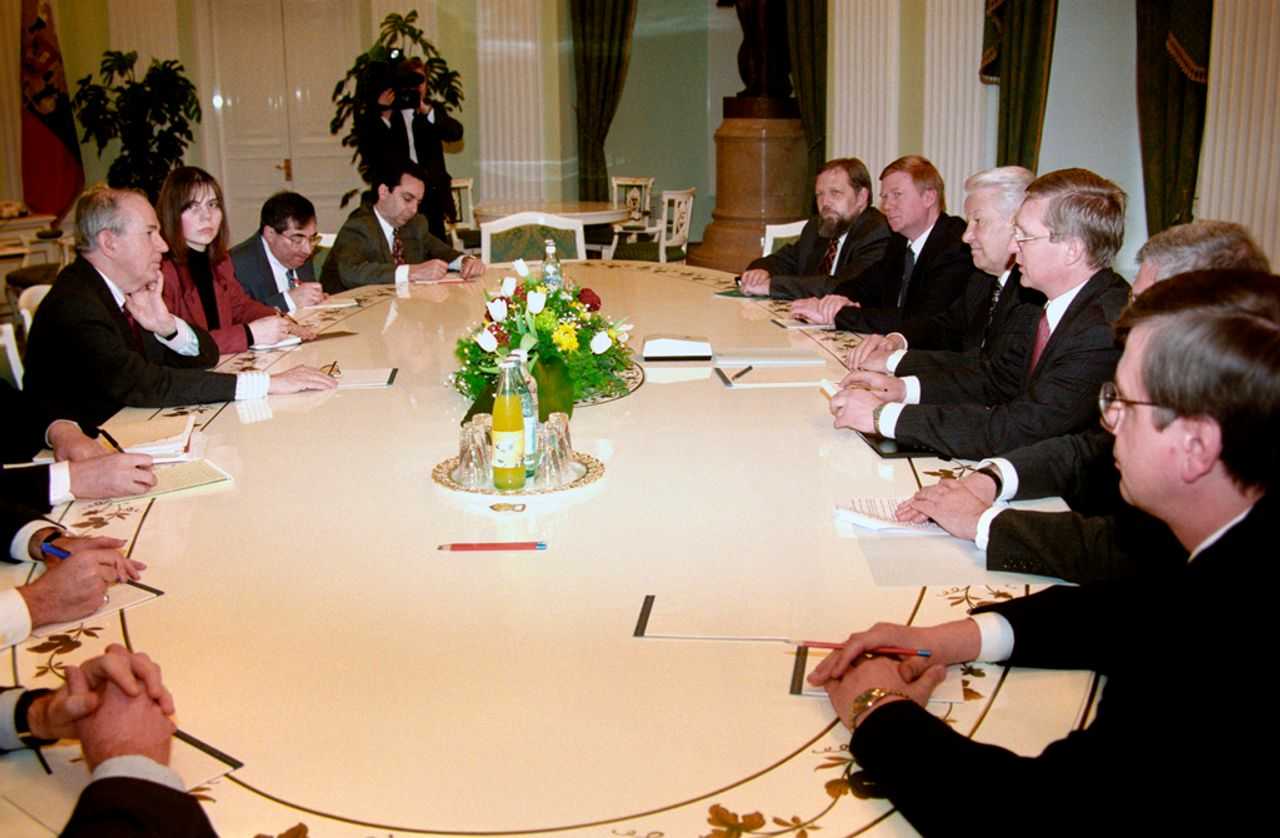
වසර 25 කට පෙර: රහස් ලේඛන මගින් නැගෙනහිර ටිමෝරයේ අපරාධ පිළිබඳව විට්ලම්ගේ කම්කරු ආන්ඩුවේ සබඳතා හෙලි කරයි
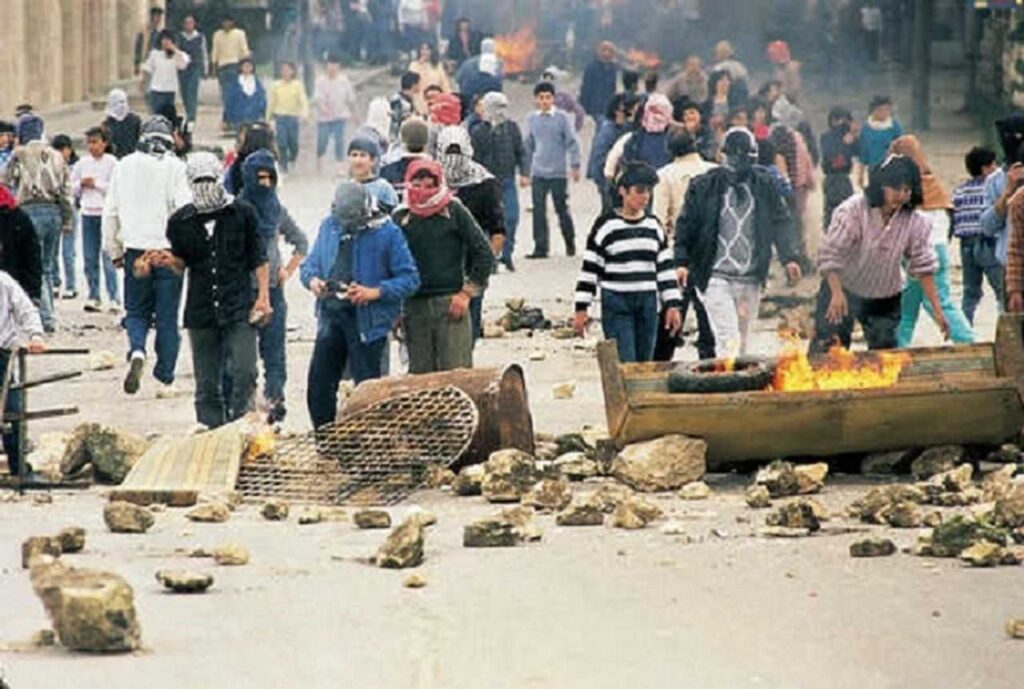
1998 අගෝස්තු 24 දින, සිඩ්නි මෝනිං හෙරල්ඩ් (Sydney Morning Herald) පුවත් පත විසින් කලින් යටපත් කරන ලද ලේඛනවල වාර්තාවක් මගින් ප්රකාශයට පත් කළේ, ඕස්ට්රේලියාවේ විට්ලම්ගේ ලේබර් ආන්ඩුව, ඉන්දුනීසියානු හෝ ඉන්දුනීසියානු පිටුබලය ලත් හමුදා විසින් ඕස්ට්රේලියානු රූපවාහිනී ප්රවෘත්ති කරුවන් පස් දෙනෙකු ඝාතනය කරන ලද බලිබෝ (Balibo) හි මූලික ප්රහාරයක් ඇතුළු , 1975 දී නැගෙනහිර ටිමෝරයට සිදු කල ඉන්දුනීසියානු ආක්රමණය සඳහා සූදානම් වීම පිළිබඳව සමීපව දැනුවත් වූ බවත්, එමෙන්ම ඕස්ට්රේලියානු ආණ්ඩුව ආක්රමණයට තම හවුල්කාරිත්වය සැඟවීමට බලිබෝ මරණ පිලිබඳ තම දැනුම වසන් කල බවත්ය.
ගොෆ් විට්ලම් 1972 දී දේශනයක් පවත්වයි වාර්තාව අවධානයට යොමු කළේ බලිබෝ නම් මායිම් ගම්මානයට එල්ල වූ ප්රහාරය පිළිබඳ ආන්ඩුවේ සවිස්තරාත්මක පූර්ව දැනුම කෙරෙහි ය. නමුත් ලේඛන මගින් ලේබර් ආන්ඩුව ආක්රමණයට සක්රීය මැදිහත්වීම සහ ලිබරල් සහ කම්කරු ආන්ඩු විසින් පවත්වාගෙන ගිය වසන් කිරීම පිලිබඳ පුළුල් ප්රශ්න වෙත යොමු විය.
ඉන්දුනීසියානු පාලන සමයේදී ඝාතනයට ලක්වූ නැගෙනහිර ටිමෝර වැසියන් 200,000ක් සමඟ එක්ව, චැනල් 7 සහ චැනල් 9 ප්රවෘත්ති කාර්ය මණ්ඩලයේ සාමාජිකයින් පස් දෙනෙක් කම්කරු ආන්ඩුවේ ප්රතිපත්තියේ ගොදුරු බවට පත් වූහ.සුහර්තෝ ආඥාදායකත්වය විසින් කලින් පෘතුගීසි යටත් විජිතයක් වූ මෙය අත්පත් කර ගැනීම පිළිබඳව කැන්බරා වෙත කෙතරම් සමීපව දැනුවත් වී තිබුණේද යත්, ප්රහාරය ආරම්භ වන බලිබෝ ඇතුළු නිශ්චිත ස්ථාන තුන එය දැන සිටි බව හෙළිදරව් කිරීම් පෙන්වා දුන්නේය.බලිබෝ අල්ලා ගැනීම , 1975 දෙසැම්බර් 7 වන දින , පූර්ණ පරිමාණ නාවික බෝම්බ හෙලීම, ගුවන් බෝම්බ හෙලීම සහ දැවැන්ත හමුදා පැමිණීමේ පූර්වගාමියා විය.
ඉන්දුනීසියානු බුද්ධි අංශ නිලධාරීන් ජකර්තාහි ඕස්ට්රේලියානු තානාපති කාර්යාල නිලධාරීන්ට 1975 ඔක්තෝබර් මැද භාගයේදී බලිබෝ ප්රහාරයේ අවසන් තොරතුරු ලබා දුන්නේය. බලිබෝ මෙහෙයුමට දින තුනකට පෙර 1975 ඔක්තෝම්බර් 13 වන දින තානාපති කාර්යාලය කැන්බරා වෙත කේබල් පණිවිඩයක් මගින් තොරතුරු ලබා දුන්නේය. ඕස්ට්රේලියානු ප්රවෘත්ති කාර්ය මණ්ඩලය නැගෙනහිර ටිමෝරයේ සිටින බව විදේශ කටයුතු දෙපාර්තමේන්තුව දැන සිටි නමුත් රූපවාහිනී මධ්යස්ථාන දෙකේ කළමනාකාරීත්වයට හෝ ප්රවෘත්ති කාර්ය මණ්ඩලයට කිසිදු අනතුරු ඇඟවීමක් කර තිබුණේ නැත.
හෙරල්ඩ් හි පළ වූ හෙළිදරව් කිරීම් වලට පෙර, විට්ලම් රජය ඉන්දුනීසියානු ආක්රමණය දිරිමත් කර ඇති බව දැන සිටියේය. නැගෙනහිර ටිමෝරය ඉන්දුනීසියාවට ඒකාබද්ධ කිරීමට ඕස්ට්රේලියානු රජය සහාය දෙන බව , 1974 තරම් මුල් භාගයේදී, විට්ලම්, ජකර්තා හි පැවති රැස්වීමකදී ජෙනරාල් සුහර්තෝට පෞද්ගලිකව පවසා තිබුණි. 1975 අප්රේල් මාසයේදී උතුරු ඕස්ට්රේලියානු නගරයක් වන ටවුන්ස්විල්හිදී ටිමෝරයේ ප්රශ්නය ගැන සාකච්ඡා කිරීම සඳහා සුහර්තෝ සමඟ තවත් රැස්වීමක් විට්ලම් පැවැත් වූ බව ද දැන ගත හැකි විය. කෙසේ වෙතත්, 1997 දී ප්රකාශයට පත් කරන ලද පොතක, විට්ලම් තම රජය , මෙම ආක්රමණය පිළිබඳව පූර්ව දැනුමක් නොමැති බව යන , තම රජයේ ප්රසිද්ධ ප්රකාශය පවත්වා ගෙන ගියේය. “බාලිබෝ හි දේශසීමා හරහා සිදු වූ ආක්රමණය ගැන අපි දැන සිටියේ නැත,” විට්ලම් ඔහුගේ ” ස්ථාවර අවශ්යතාවයන්” (Abiding Interests) වෙළුමේ ලිවීය.
පුවත්පතේ විදේශ කර්තෘ හමිෂ් මැක්ඩොනල්ඩ් විසින් ඉදිරිපත් කරන ලද තොරතුරු පෙන්නුම් කළේ, 1974 අගභාගයේ සිට, පළමු සුහර්තෝ-විටලම් හමුවෙන් පසුව, බලහත්කාරයෙන් භූමිය අල්ලා ගැනීමේ ඉන්දුනීසියාවේ අභිප්රාය සම්බන්ධ තොරතුරු,
ඉන්දුනීසියානු නිලධාරීන් විසින් නිතිපතා ඕස්ට්රේලියානු තානාපති කාර්යාලයට සැපයූ බවයි.
වසර 50 කට පෙර: කැනේඩියානු දුම්රිය සේවකයෝ ජාතික වැඩ වර්ජනයක් ආරම්භ කරත
1973 අගෝස්තු 23 වන දින, කැනේඩියානු දුම්රිය සේවකයින් රැකියාවෙන් ඉවත් වී, දුම්රිය සමාගම් 11 කට එරෙහිව රටපුරා වැඩ වර්ජනයක් ආරම්භ කළහ. එම සමාගම් අතරින් විශාලතම ඒවා වූයේ , කැනේඩියානු ජාතික දුම්රිය සහ කැනේඩියානු පැසිෆික් දුම්රිය යන සමාගම්ය. වැඩවර්ජනය කැනේඩියානු ආර්ථිකය කැටි කළ අතර, කාර්මික හා කෘෂිකාර්මික භාණ්ඩ ප්රවාහනය වහාම නතර විය. එය උද්ධමනය විසින් මෙහෙයවනු ලබන උතුරු ඇමරිකාව සහ ලෝකය පුරා කම්කරුවන්ගේ දැවැන්ත වැඩ වර්ජන රැල්ලක කොටසකි.
වාර්තාගත උද්ධමනයට සරිලන ආකාරයට දුම්රිය කම්කරුවන් වසර දෙකක කොන්ත්රාත්තුවේ ආයු කාලයට වඩා සියයට 21.6කින් පඩි වැඩි කිරීමක් ඉල්ලා සිටියහ. 1973 සිට 1975 දක්වා උද්ධමන අනුපාතය වසරකට සියයට 10 කට වඩා වැඩි විය. දුම්රිය සමාගම් වසර දෙකක කොන්ත්රාත්තුවට සියයට 14ක පමන පඩි වැඩි වීමක් ලබා දෙමින් උද්ධමනයට වඩා ඉහල වැටුප් වැඩිවීමක් ලබා දීම ප්රතික්ෂේප කර තිබුණි.
ද බුලටින් හි 1973 සැප්තැම්බර් 3 සංස්කරණයේ සිරස්තල වර්ජනයේ බලපෑම දුම්රිය සමාගම්වලට පමණක් සීමා නොවීය. මෝටර් රථ නිෂ්පාදකයින් වන ජෙනරල් මෝටර්ස් සහ ෆෝඩ් සමාගම් වල තෙරේස්, ඔෂාවා ඕක්විල් සහ ස්ටී හි කම්හල්වල නිෂ්පාදනය නතර කිරීමට බල කෙරුනි.
වැඩ වර්ජන කල දුම්රිය කම්කරුවන් 56,000, බොහෝ දුරට පෝටර් සහ දුම්රිය අංගන කම්කරුවන්, සමස්ත කැනේඩියානු දුම්රිය ශ්රම බලකායෙන් එක් කොටසක් පමනක් විය. දුම්රිය කර්මාන්තයේ විවිධ මෙහෙයුම්වල සංවිධානය වූ අතිරේක කම්කරුවන් 100,000ක් මහා වැඩ වර්ජනයක වාතාවරණයක් නිර්මානය කරමින් පිකට් සීමාවන් තරණය කිරීම ප්රතික්ෂේප කළහ. කැනේඩියානු කම්කරු පන්තිය පුරා සහයෝගීතාවයේ ක්රියාවන් වර්ජනය පවතින අතරතුර පැවති අතර, රේල් පීලි මත කිසිදු භාණ්ඩයක් ගෙන නොයාම සහතික විය.
1950 සහ 1966 දී කැනේඩියානු දුම්රිය සේවකයින් විසින් කරන ලද පෙර පැවති ජාතික වැඩ වර්ජන දෙකේදී මෙන්, කැනේඩියානු ආන්ඩුව ඉක්මනින්ම වැඩ වර්ජන කඩ කිරීමේ නීති සම්මත කිරීමට පියවර ගනිමින් , කම්කරුවන්ට ගිවිසුමකට ඇතුළු වීමට බල කරන ලදී. වැඩවර්ජන තහනමක් සම්මත කිරීම සඳහා කැනේඩියානු පාර්ලිමේන්තුව අගෝස්තු 30 වැනි දින විශේෂ සැසිවාරයකදී රැස්විය.
ආන්ඩුව විසින් සහන කොන්ත්රාත්තුවක් පැනවීමට විරෝධය දැක්වීම සඳහා කැනඩාව පුරා සිටි , ඔටාවා වෙත ගමන් කළ කෝපාවිෂ්ඨ දුම්රිය කම්කරුවන්ගේ මහජන පෙලපාලි වලට ඔවුන්ට මුහුණ දීමට සිදුවිය. පුවරු රැගෙන ගිය සමහර කම්කරුවන් විසින් “පාර්ලිමේන්තු මන්ත්රීවරු වර්ජනය බිද නොදැමිය යුතුය” යනුවෙන් කියමින් ලිබරල් අගමැති පියරේ එලියට් ටෘඩෝ ඉවත් කරන ලෙස ඉල්ලා සිටියහ.
ප්රංශයේ 1968 මැයි මහා වැඩ වර්ජනයෙන් සහ ලොව පුරා අනෙකුත් ප්රධාන කම්කරු පන්ති ප්රහාරවලින් ආශ්වාදයක් ලැබූ බොහෝ තරුණ සටන්කාමී කම්කරුවන් මෙම පෙලපාලියට ඇතුලත් විය. එක් අවස්ථාවකදී දුම්රිය සේවකයන් පාර්ලිමේන්තුවේ ආරක්ෂාවට සිටි මවුන්ටීස් [ කැනේඩියානු ෆෙඩරල් හා ජාතික පොලිස් සේවය] භට පෙළ කඩාගෙන ගොඩනැගිල්ලට ඇතුළු විය. පොලිසිය අවසානයේ කම්කරුවන් ඉවත් කිරීමට පෙර පාර්ලිමේන්තු ගොඩනැගිල්ලේ සමහර ජනෙල් කඩා දැමීම ඇතුළු සමහර සටන් ඇති විය.
වර්ජනය අතරතුර දුම්රිය සේවකයන් ඉමහත් නිර්භීතකම සහ සහයෝගීතාව පෙන්නුම් කළ අතර, ඊට සම්බන්ධ වූ වෘත්තීය සමිති හතෙන් විශාලතම සමිතිය වූයේ දුම්රිය සහ ගුවන් ලිපිකරුවන්ගේ සහෝදරත්වය (BRAC) යි. සමිති ප්රධානීන්, වැඩ වර්ජන කඩ කිරීමේ නීති සම්මත කිරීමට ආන්ඩුව මැදිහත් වීම ගැන කිසිදු ප්රශ්නයක් මතු කර ගත්තේ නැත. “නීති සම්පාදනයේ වටිනා විසඳුමක් තිබේ නම්, ඒවා ආපසු ලබා ගැනීමේදී කිසිදු ගැටළුවක් ඇති නොවේ” යැයි වෘත්තීය සමිති කේවල් කිරීමේ කමිටුවේ සභාපති රිචඩ් ස්මිත් පැවසීය.
වැඩවර්ජනයේ දින නවයකට පසුව, සැප්තැම්බර් 1දා පාර්ලිමේන්තුව වර්ජන කඩකිරීමේ නීතිය සම්මත කලේ, සමාගමේ මූලික දීමනාවට වඩා පැයකට යන්තම් ශත 4ක වැටුප් වැඩිවීමක් ලබා දෙමිනි. වෘත්තීය සමිති නායකයෝ වර්ජන කඩ කිරීමේ නීතියට කිසිදු ප්රතිරෝධයක් නොදැක්වූ අතර කම්කරුවන්ට නැවත රැකියාවට යාමට නියෝග කළහ.
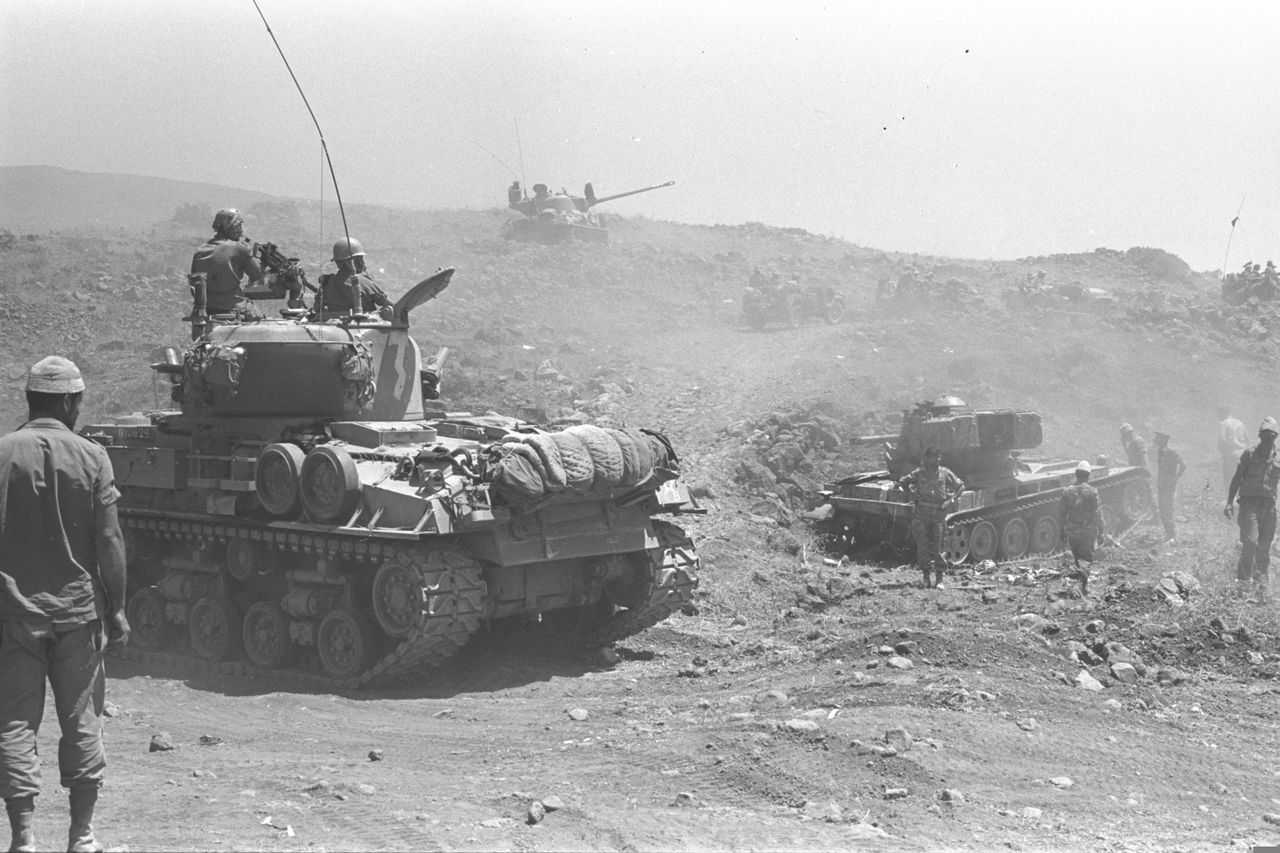
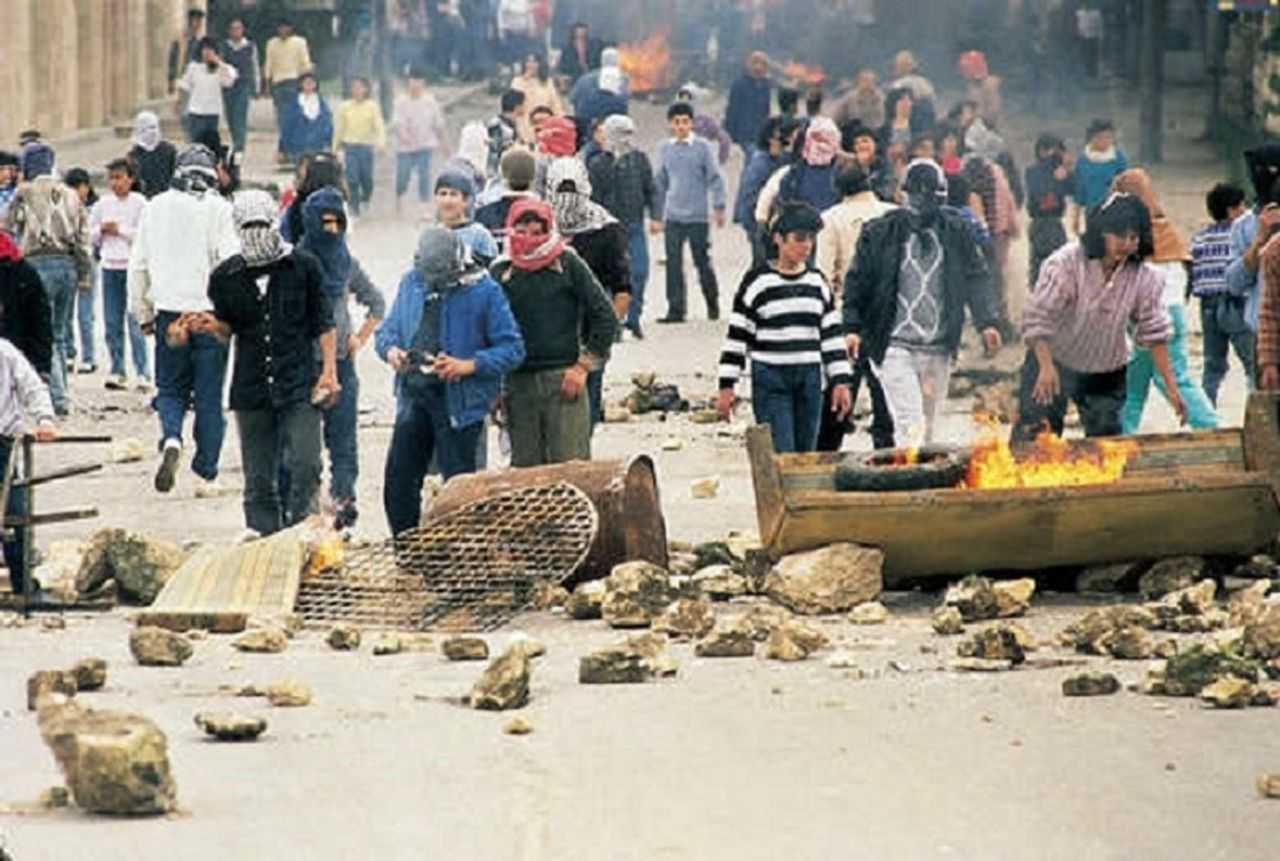
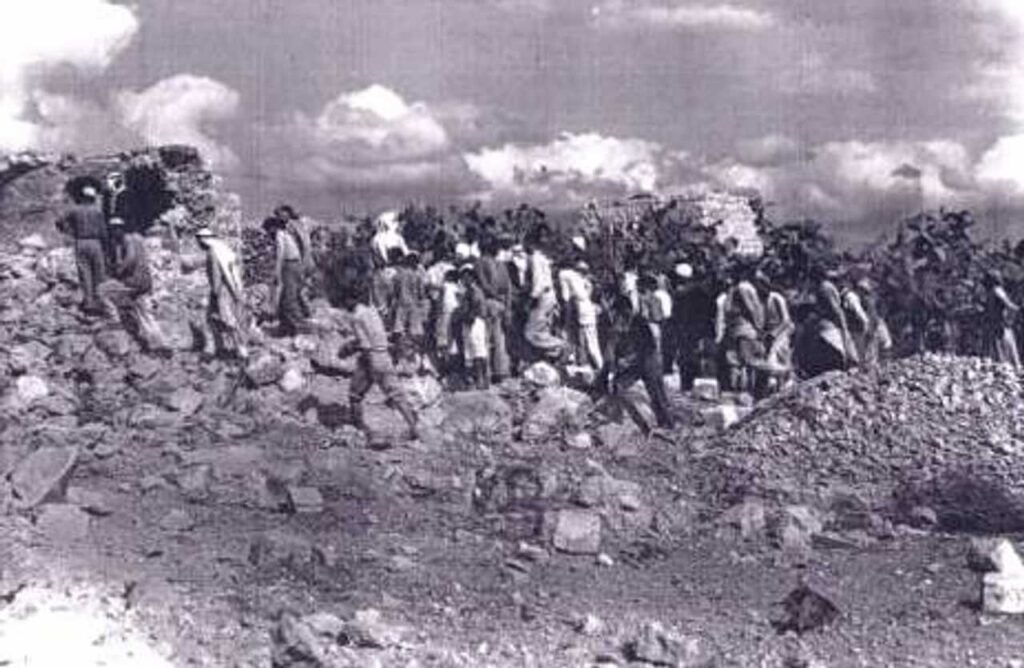
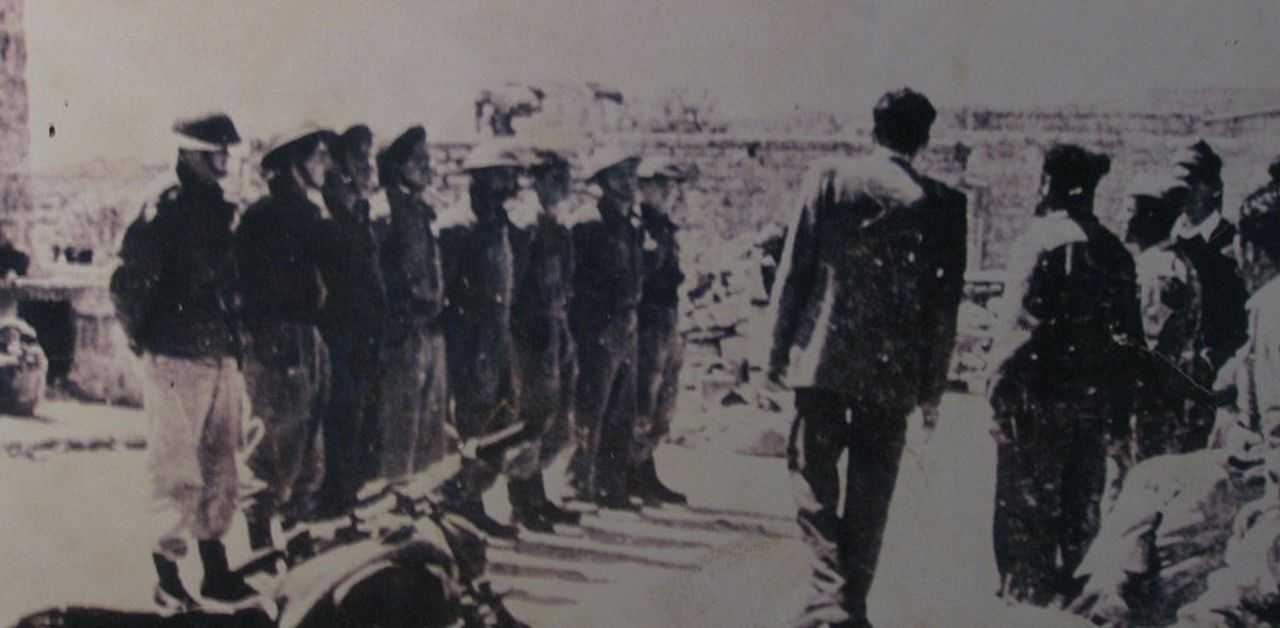
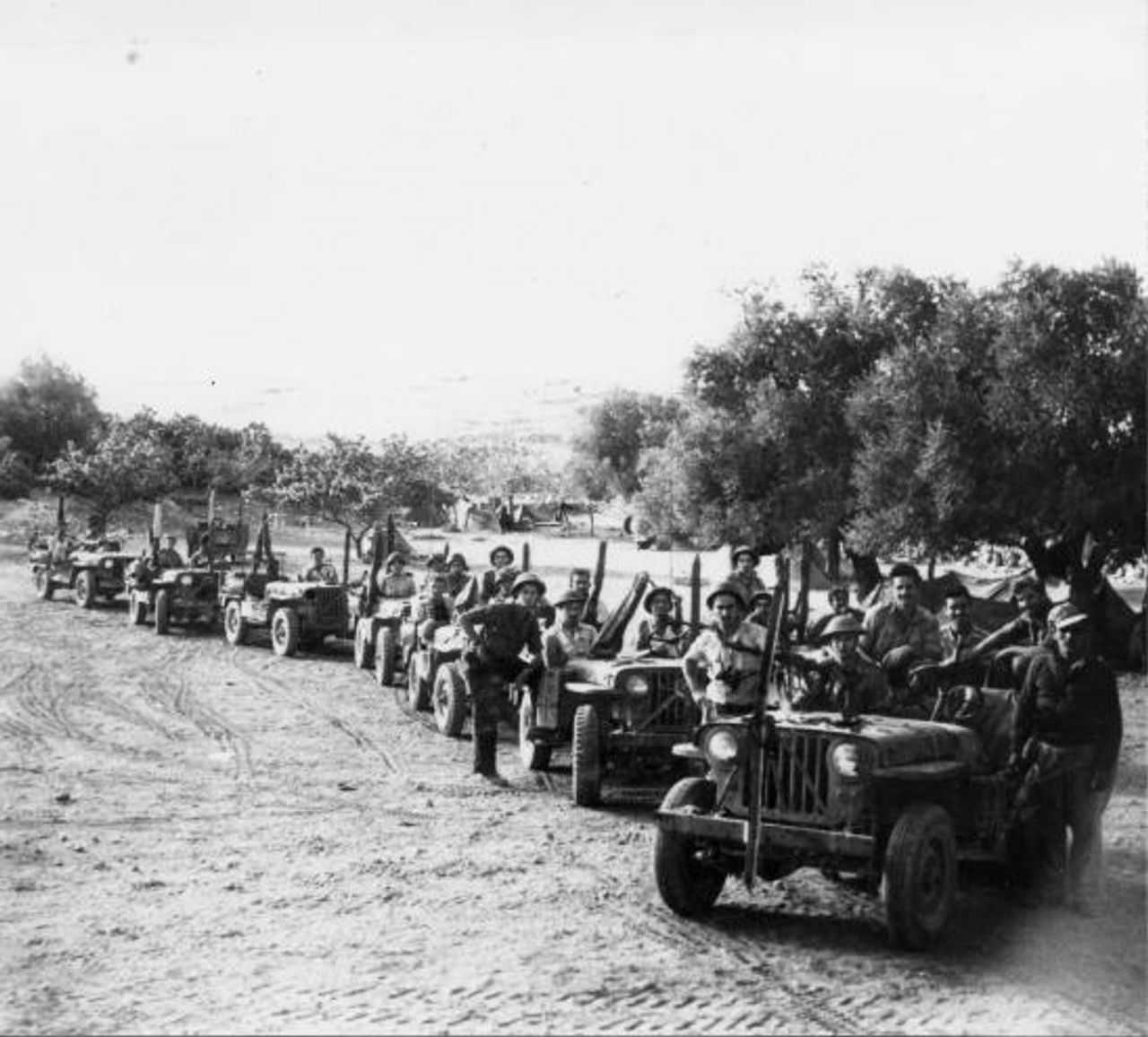
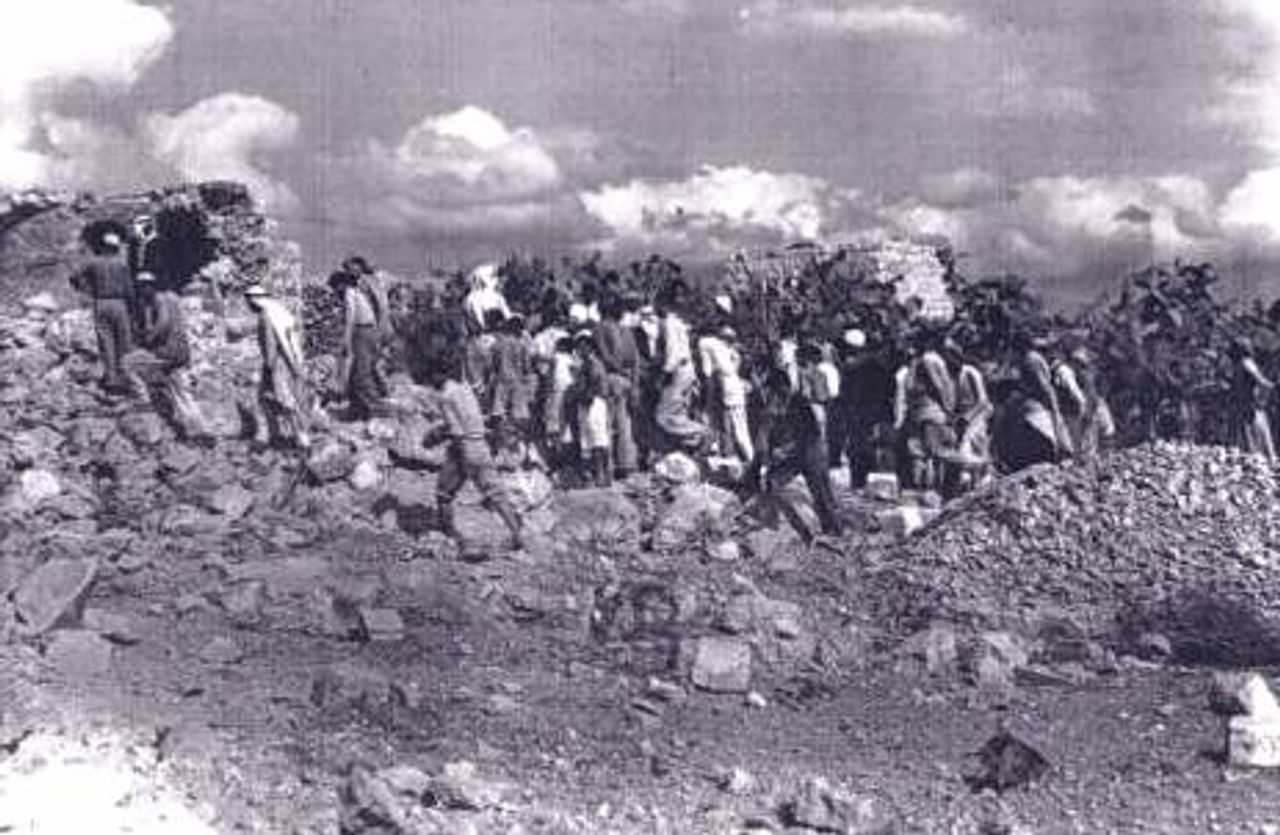
වසර 75කට පෙර: ඊශ්රායල හමුදාව “ඩ්රාෆ්ට් ඩෝජර්ස්” මර්දනය දියත් කරයි
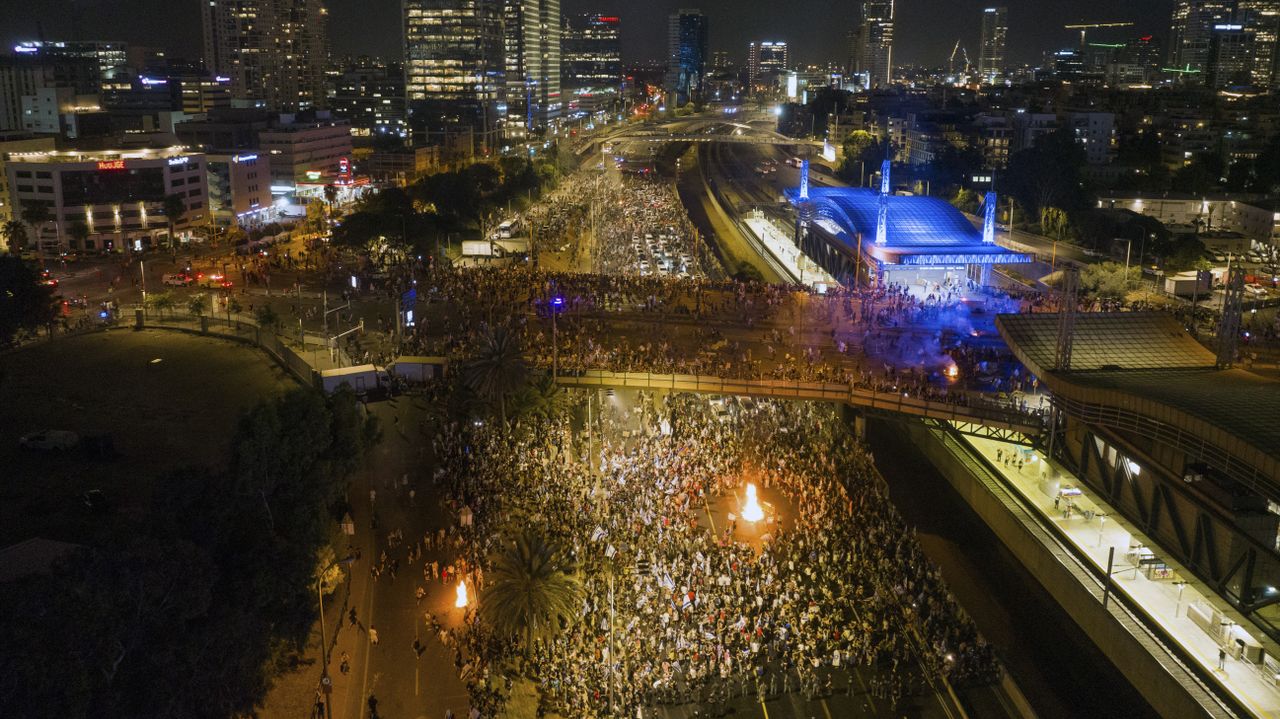
1948 අගෝස්තු 22 දින, ඊශ්රායල සන්නද්ධ හමුදා විසින් පලස්තීන ජනතාව සහ අරාබි රාජ්යයන්ගේ සභාගයක් මගින් යුද්ධයට අභ්යන්තරව දැක් වූ විරුද්ධත්වයට එරෙහිව කුරිරු මර්දනයක් දියත් කළහ. ඊශ්රායලයේ දෙවන වැඩිම ජනගහණයෙන් යුත් නගරය වූ ටෙල් අවිව් තත්ය යුද නීතිය යටතේ සහ ඇඳිරි නීතිය යටතේ තබා තිබූ අතර, සන්නද්ධ මුර සංචාර හරහා යුද්ධයට සහභාගී නොවූ අය සොයමින් ගමන් කරන ලදී. මෙහෙයුම “බෙට්සර්” හෝ “ශක්තිය” ලෙස නම් කර තිබුණි.
එතරම් ප්රසිද්ධ නොවූ මෙම ප්රහාරය ඊශ්රායල් රාජ්යයේ කුරිරු පදනම් අවධාරනය කරයි. බ්රිතාන්ය පලස්තීනයෙන් ඉවත් වීම සහ මැදපෙරදිග මෙහෙයුම් සඳහා වෙරළ තීරයක් පිහිටුවීමට ඇමරිකානු අධිරාජ්යවාදයේ අධිෂ්ඨානයේ ප්රතිඵලයක් ලෙස, ඒ වන විට , මාස හයකටත් අඩු කාලයකට පෙර, එනම් මැයි මාසයේදී, ඊශ්රායල් රාජ්ය පිහිටුවන ලදී.
පලස්තීන අරාබිවරුන් ජනගහනයෙන් බහුතරයක් වුවද , නව ඊශ්රායල රජය තුල ආධිපත්යය දැරු , සියොන්වාදී බලවේග විසින් යුදෙව් ආධිපත්ය සහිත රාජ්යයකට සහාය දෙන ලෙස බ්රිතාන්යයට බලපෑම් කිරීමේ අරමුණින් ත්රස්තවාදී ව්යාපාරයක් දියත් කරන ලදී . සියොන්වාදී නායකයින් යුදෙව් රාජ්යයක් ලෙස ඊශ්රායලයේ වාර්ගික-ආගමික ස්වභාවයට අනුකූලව, හැකිතාක් අරාබිවරුන් පලවා හැරීම සඳහා වාර්ගික ශුද්ධ කිරීමේ ව්යාපාරයක නිරත විය. ඊශ්රායල් රාජ්ය පිහිටුවීම ප්රකාශය කිරීමත් සමඟම අසල්වැසි අරාබි රාජ්යයන් විසින් ක්ෂනික යුද ප්රකාශයක් කිරීම මගින් , සියොන්වාදී නායකයින් සහ ඔවුන්ගේ අධිරාජ්යවාදී ආධාරකරුවන් විසින් අපේක්ෂා කළ දේ ඉටු වී තිබුණි.
ඊශ්රායලය විධිමත් ලෙස පිහිටුවීමට පෙර, සියොන්වාදී නායකත්වය විසින් 1947 අග භාගයේදී අර්ධ අනිවාර්ය හමුදා බඳවා ගැනීමේ ක්රමයක් හඳුන්වා දී තිබුණි. හමුදාවට බැදීමට සුදුසු වයසේ සිටින පිරිමින් සන්නද්ධ මිලීෂියාවන්ට බැඳීමටත් , ඔවුන් , සියොන්වාදී නායකත්වයේ අණ පිළිපැදීමත් බලාපොරොත්තු විය. නිදහස පිළිබඳ මැයි ප්රකාශයෙන් පසුව, මෙම ක්රමය විධිමත් කරන ලදී.
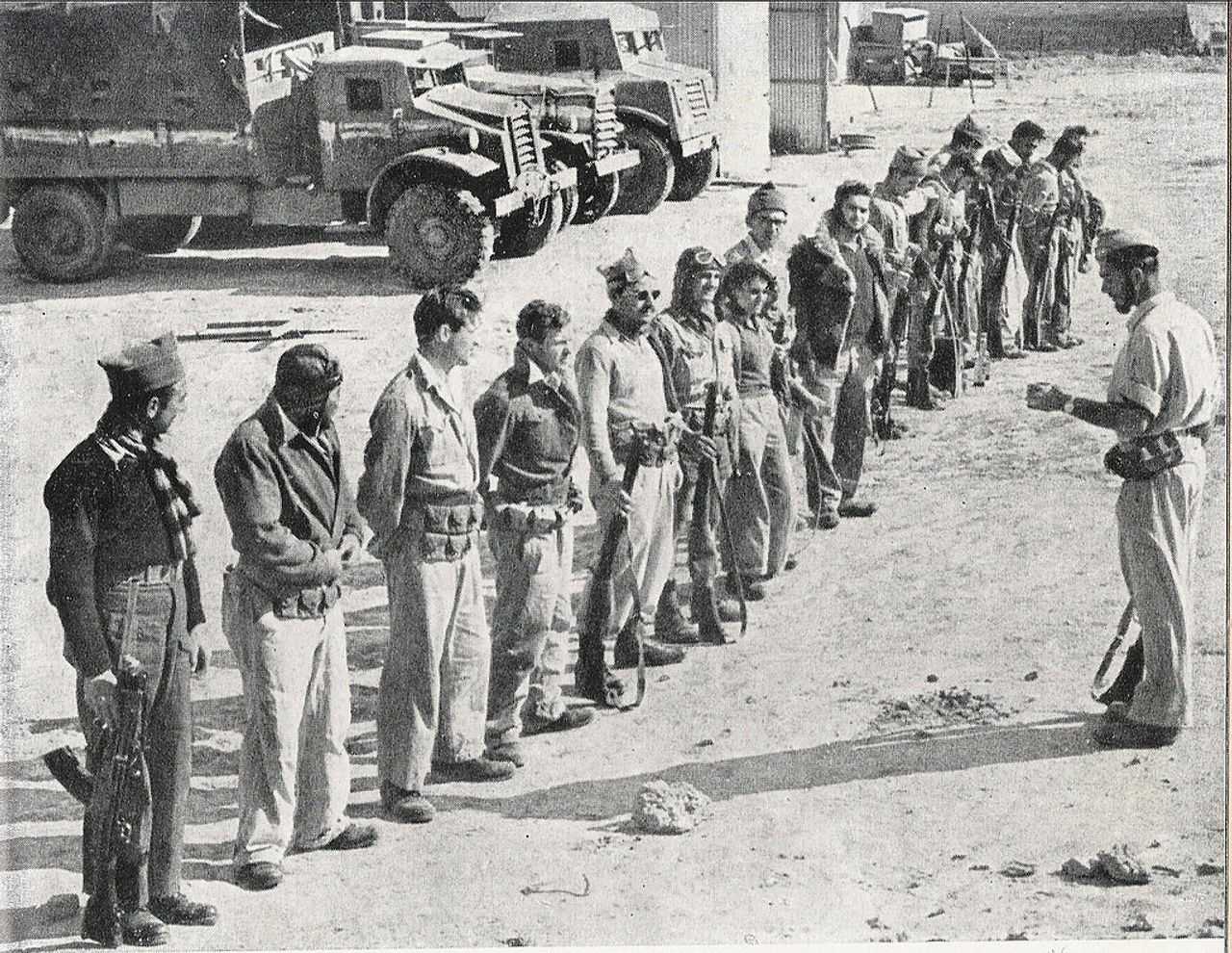
අගෝස්තු මාසයේදී, ඊශ්රායල රජය, අභ්යන්තර මර්දනය දියත් කිරීම සඳහා අරාබි රාජ්යයන් සමඟ සටන් සන්සුන් වීමේ අවස්ථාව ලබා ගත්තේය. පෙනී සිටීමට අපොහොසත් වුවහොත් අත්අඩංගුවට ගැනීමේ තර්ජනය යටතේ , වයස අවුරුදු 17-50 අතර සියලුම පිරිමින්ට සහ 18-35 සියලුම කාන්තාවන්ට ටෙල් අවිව්හි බඳවා ගැනීමේ මධ්යස්ථාන 20කට යන ලෙස උපදෙස් දෙන ලදී,
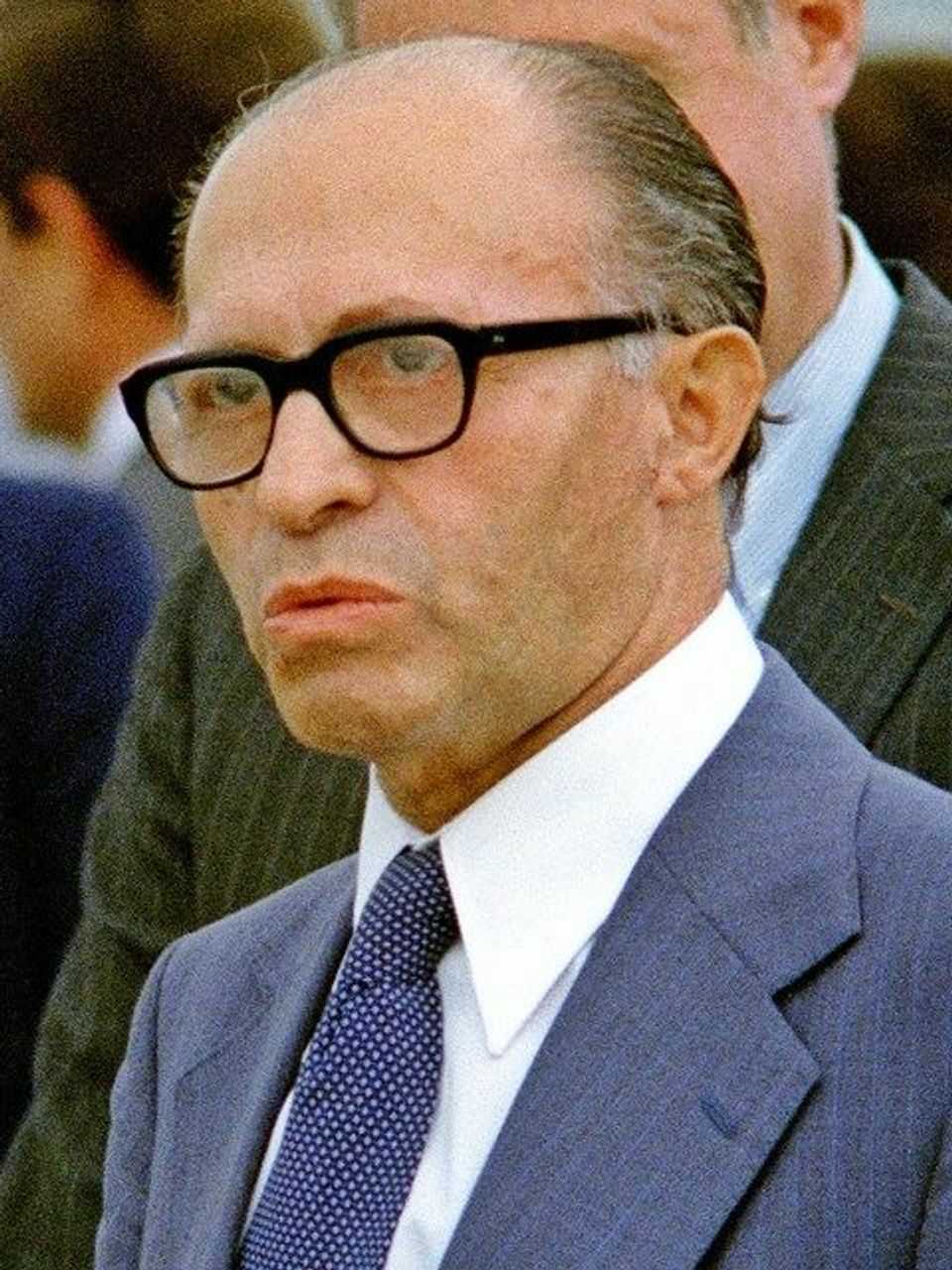
1948 මැදිහත් වීමකට පෙර ඊශ්රායල සොල්දාදුවන් දැනුවත් කිරීම දින පහක් පුරා නගරයේ ඇඳිරි නීතිය පනවා තිබුණි. එහිදී ,ඊශ්රායල අගමැති ඩේවිඩ් බෙන්-ගුරියන් විසින් ආරම්භ කරන ලද හගානාා හි කිරියාති බළකාය විසින් මෙහෙයවන ලද සොල්දාදුවන් මුර සංචාරයේ යොදවා තිබුණි .
හමුදාව ගෙයින් ගෙට ගියේය . අධිකරණ වරෙන්තුවක් නොමැතිව ඕනෑම නිවසකට බලහත්කාරයෙන් ඇතුළු වීමේ අයිතිය ඔවුන්ට ලබා දී තිබුණි. අසල්වැසියන්ට එකිනෙකාට දැනුම් දීමට දිරිගන්වන ලදී. අරාබි යුද ප්රයත්නයට ආධාර කරන “ඩ්රාෆ්-ඩෝජර්” ද්රෝහීන් ලෙස ලේබල් කරන ප්රකාශයන් සමඟින්, දක්ෂිණාංශික හිස්ටීරියාවේ ප්රවාහයක් මධ්යයේ මෙහෙයුම සිදු කරන ලදී.
පිරිමින් 1,044 ක් සහ කාන්තාවන් 1,720 ක් ඇතුළු පුද්ගලයන් 2,764 ක්, අත්අඩංගුවට ගෙන තිබුණි. මුළු සංඛ්යාවෙන් 1,000 කට පමණ වහාම සන්නද්ධ සේවාවන්ට ඇතුළත් වන ලෙස නියෝග කරන ලදී.නමුත්, කල් දැමූ කෙටුම්පතක් යටතේ, තවත් 1,500 දෙනෙකුට බඳවා ගැනීමට උපදෙස් දී තිබුණි . 200 කට වැඩි පිරිසක් පලා ගිය අය ලෙස සිර කරන ලදී.
වසර 100 කට පෙර: ඉතාලිය ග්රීසියට තර්ජනය කිරීම සඳහා “කෝර්ෆු සිද්ධිය” යොදා ගනී
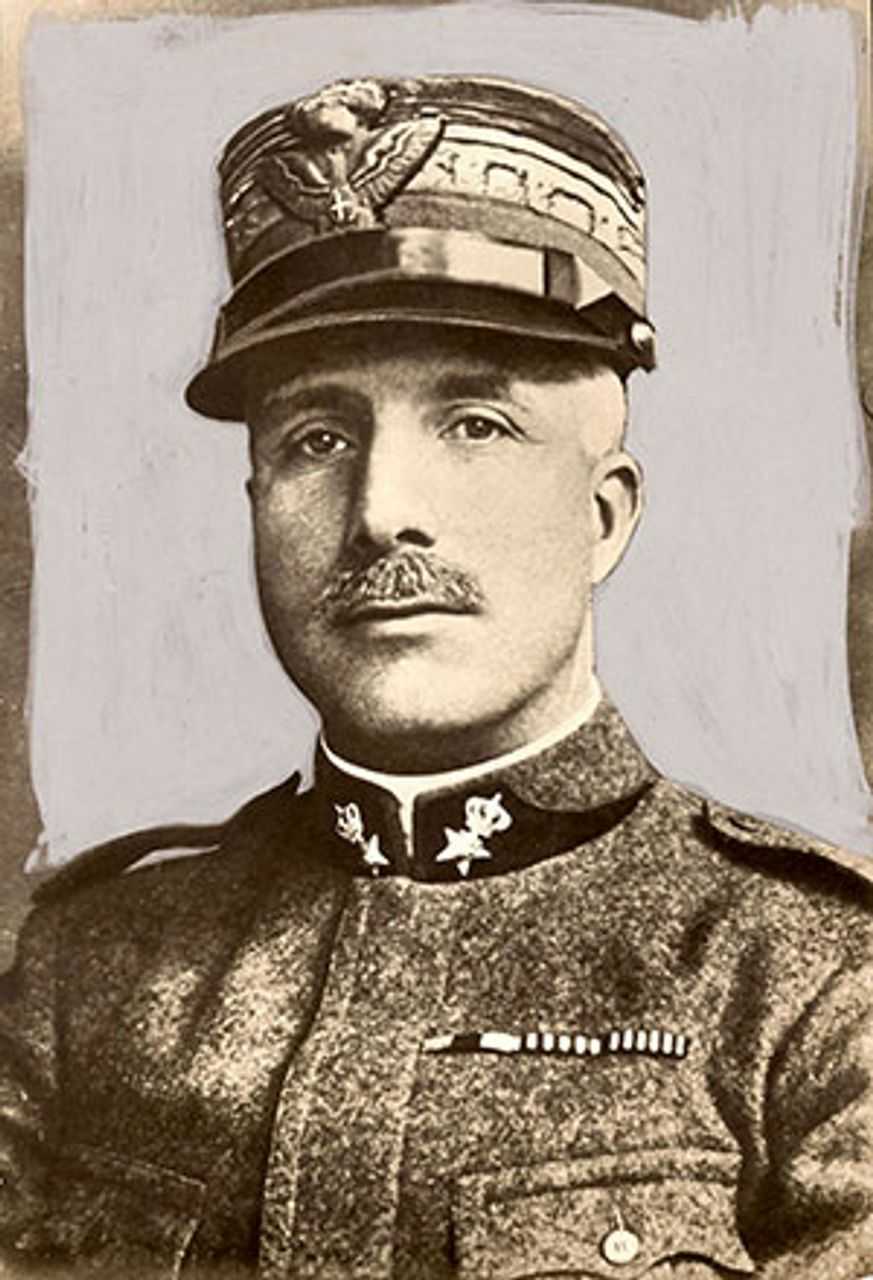
1923 අගෝස්තු 27 වන දින ඉතාලි හමුදාවේ ජෙනරාල්වරයෙකු වූ එන්රිකෝ ටෙලිනි ඇල්බේනියානු දේශසීමාව අසල ග්රීක නගරයක් වන අයෝනිනා නගරයෙන් පිටතදී ඝාතනය කරන ලදී. ඒ සමගම, ඔහුගේ සගයන් 4 දෙනෙකු ද මරා දමා තිබුණි. ග්රීසිය සහ ඇල්බේනියාව අතර ඇති වූ මායිම් ආරවුලක් හේතුවෙන් ටෙලිනි එම ප්රදේශය පරීක්ෂා කරන ජාතීන්ගේ සංගමයේ නියෝජිත කණ්ඩායමකට අයත් විය. ඇල්බේනියානු රජය ග්රීකයන්ට ද ග්රීකයන් ඇල්බේනියානු කොල්ලකරුවන්ට ද දොස් පැවරූහ. මෙහි අපරාධකරුවන් කිසි විටෙක හඳුනා ගත්තේ නැත.
මෙම සැඟව පහරදීම , එනම් “කෝර්ෆු සිද්ධිය” ලෙස ප්රසිද්ධියට පත් වූ මෙය, ඉතාලි අධිරාජ්යවාදී ආක්රමණකාරීත්වයේ ප්රේරක සිදුවීම බවට පත් විය. ටෙලිනිගේ මරණයෙන් දින කිහිපයකට පසු, ඉතාලියේ ෆැසිස්ට් ආන්ඩුව ග්රීක ආන්ඩුවට අවසාන නිවේදනයක් යවමින් නිල සමාව ඉල්ලා, වන්දි වශයෙන් ලීර් මිලියන 50 ක් සහ මිනීමරුවන් අත්අඩංගුවට ගෙන මරණ දඬුවම ක්රියාත්මක කරන ලෙස ඉල්ලා සිටියේය. ඉතාලිය තවදුරටත් ඉල්ලා සිටියේ ටෙලිනි සහ ඔහුගේ සගයන්ගේ අවමංගල්යය මුළු ග්රීක රජයේ සහභාගීත්වය ඉදිරියේ සිදු කරන ලෙසත්, ග්රීක වරායක් වන පරේයස් (Piraeus) වෙත යවනු ලබන ඉතාලි නැව්වලට , ග්රීක නාවික හමුදාව විසින් ආචාර කල යුතු බවත්ය.
ග්රීක රජය මෙම ඉල්ලීම් බොහොමයක් ප්රතික්ෂේප කළේය. ඉතාලි ආන්ඩුව විසින් ඉතාලිය තුළ ග්රීක විරෝධී මාධ්ය ව්යාපාරයක් දියත් කරන ලද අතර අගෝස්තු 31 දින, ඉතාලියේ ෆැසිස්ට් නායක බෙනිටෝ මුසෝලිනි, ඉතාලි නාවික හමුදාවේ භට පිරිසක් ඇඩ්රියාටික් මුහුදේ පිහිටි ග්රීක දූපතක් වන කෝර්ෆු වෙත යවා, මිලිටරිමය නොවන ඉලක්කයන් මාලාවකට බෝම්බ හෙලීය. තුර්කියේ සිට පැමිණි , ජනවාර්ගික ග්රීකයින් සඳහා සරණාගත මධ්යස්ථාන ඇතුළු සිවිල් වැසියන් දුසිම් ගනනක් ඉන් මරා දැමුණි.
රෝමය හමුදාව දහස් ගණනක් දිවයිනට ගොඩ බැස්ස අතර ග්රීක නැව් ගමනාගමනය සඳහා වූ මධ්යධරණී ජල මාර්ග වසා දැමීය. මුසෝලිනි, දේශනයකදී කියා සිටියේ , කෝර්ෆු දිවයින , වසර සිය ගණනක් තිස්සේ ඉතාලියේ වැනීස් ජනරජයට අයත් තිබූ බවයි. කෝර්ෆු ආක්රමණය, ඇත්ත වශයෙන්ම, අවම වශයෙන් ජූලි මාසයේ සිට මුසෝලිනි විසින් සැලසුම් කර තිබුණි.
ජාතීන්ගේ සංගමය මෙම ක්රියාව හෙළා දුටු අතර, ග්රීසිය දිගු කලක් සේවාදායක රාජ්යයක් ලෙස සැලකූ බ්රිතාන්ය අධිරාජ්යවාදය විසින් ඉතාලියට විශේෂයෙන්ම විරුද්ධ විය. සැප්තැම්බර් අග වන විට ඉතාලියානුවන් කෝර්ෆු දිවයිනෙන් ඉවත් කරනු ලැබුවේ ග්රීසිය නින්දිත කොන්දේසි මාලාවකට එකඟ වීමෙන් පසුවය.
මෙම ක්රියාව ෆැසිස්ට්වාදය යටතේ ඉතාලි අධිරාජ්යවාදයේ ව්යාප්තියේ කොටසක් වූ අතර, 1923 ට පෙර , ආරම්භ වූ යුද්ධයකදී ලිබියානු ජනගහනයෙන් හතරෙන් පංගුවකට වඩා ඝාතනය කිරීම සහ පසුකාලීනව 1935 දී ඉතියෝපියාව, 1939 දී ඇල්බේනියාව සහ 1940 දී ග්රීසිය ආක්රමන කිරීම සිදු විය . දෙවන ලෝක යුද්ධයේදී අක්ෂ බලවතුන්ගේ කොටසක් ලෙස ඉතාලි හමුදා හිට්ලර්ගේ ජර්මානු නාසි ආන්ඩුව සමග එක්ව සටන් කළහ.